CIE A Level Biology复习笔记5.1.1 Chromosome Structure翰林国际教育
What are Chromosomes? Structure of a Chromosome Pellicle Matrix Chromonemata Centromere Secondary Constriction or Nucleolar Organiser Telomeres Types of Chromosomes A. Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes B. On the Basis of Number of Centromeres C. On the Basis of Location of Centromere Prokaryotic Chromosomes Eukaryotic Chromosomes a. Nucleosomes
Genealogy Glossary Common DNA Terms Explained MyHeritage Knowledge Base
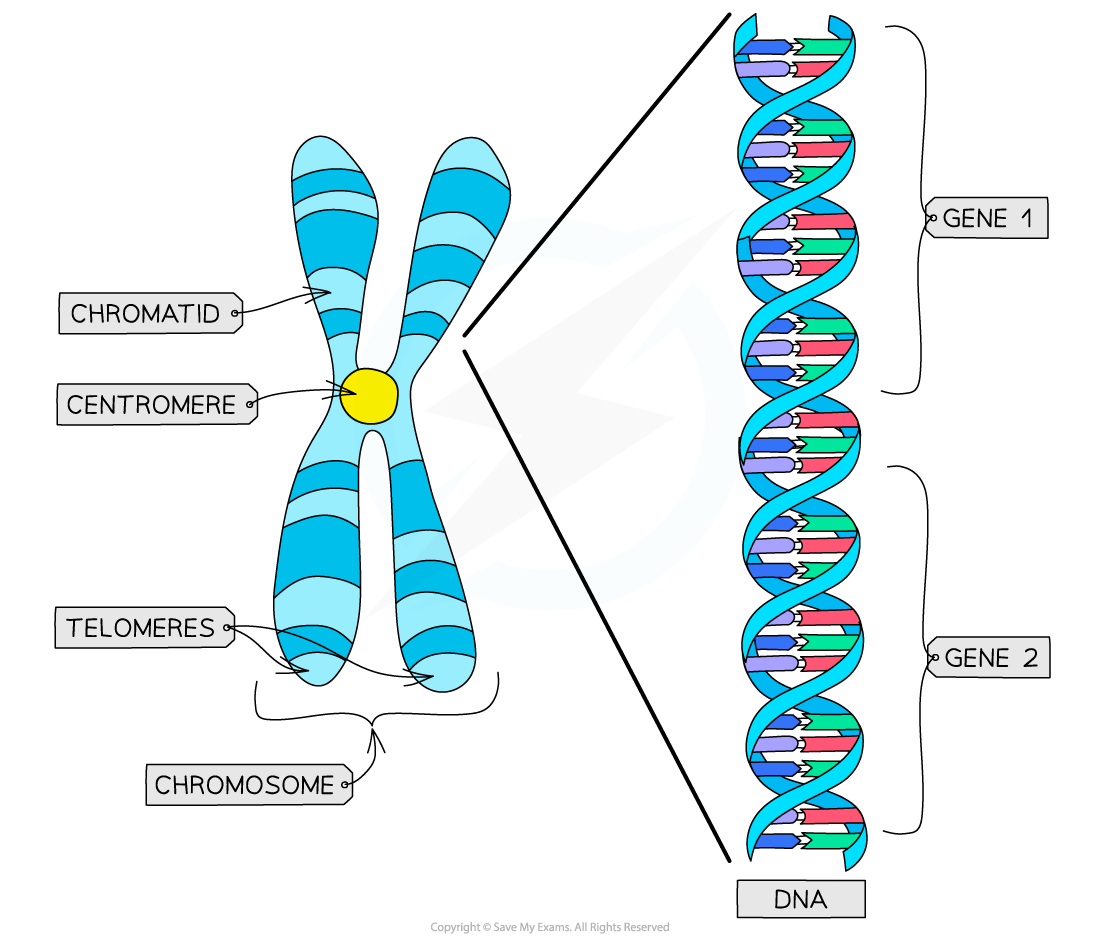
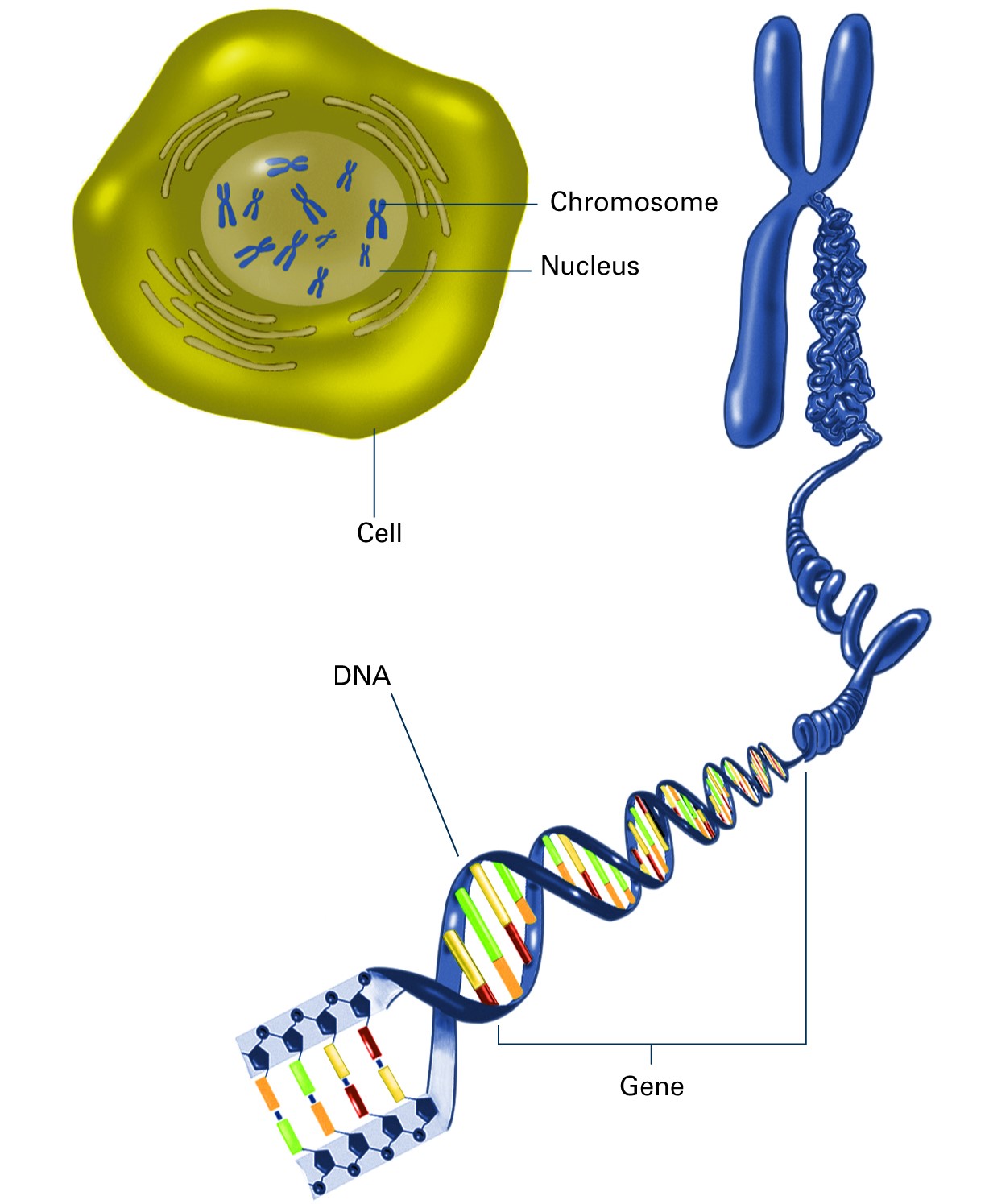
Diagram Showing Chromosome Chromosomes are usually not visible under a normal microscope. They are mostly viewable only during cell division under a light microscope. Chromosomes are tightly packed thread-like structures that are composed of DNA. These DNA are compactly coiled around proteins known as histones.
Chromosomes Fact Sheet NHGRI
The compactness of chromosomes plays an important role in helping to organize genetic material during cell division and enabling it to fit inside structures such as the nucleus of a cell, the average diameter of which is about 5 to 10 μm (1 μm = 0.00l mm, or 0.000039 inch), or the polygonal head of a virus particle, which may be in the range of.

Chromosome Structure
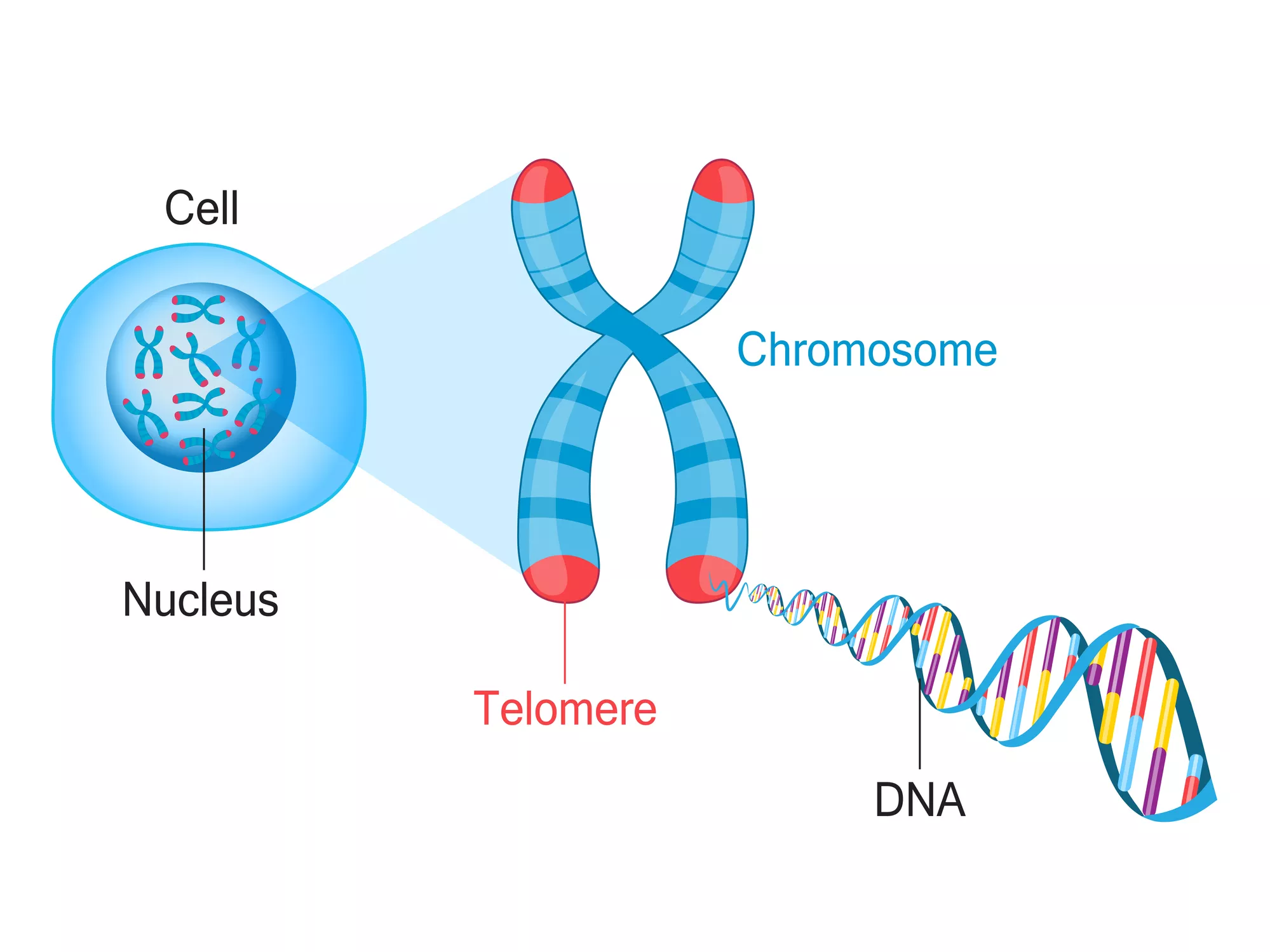
Genetics → Help Me Understand Genetics → Cells and DNA → What is a chromosome? What is a chromosome? In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that support its structure.
What Are The Parts Of A Chromosome Images and Photos finder
< Prev Next > Chromosome Map Our genetic information is stored in 23 pairs of chromosomes that vary widely in size and shape. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, X and Y, that determine our sex.

Parts of Chromosome Diagram Quizlet
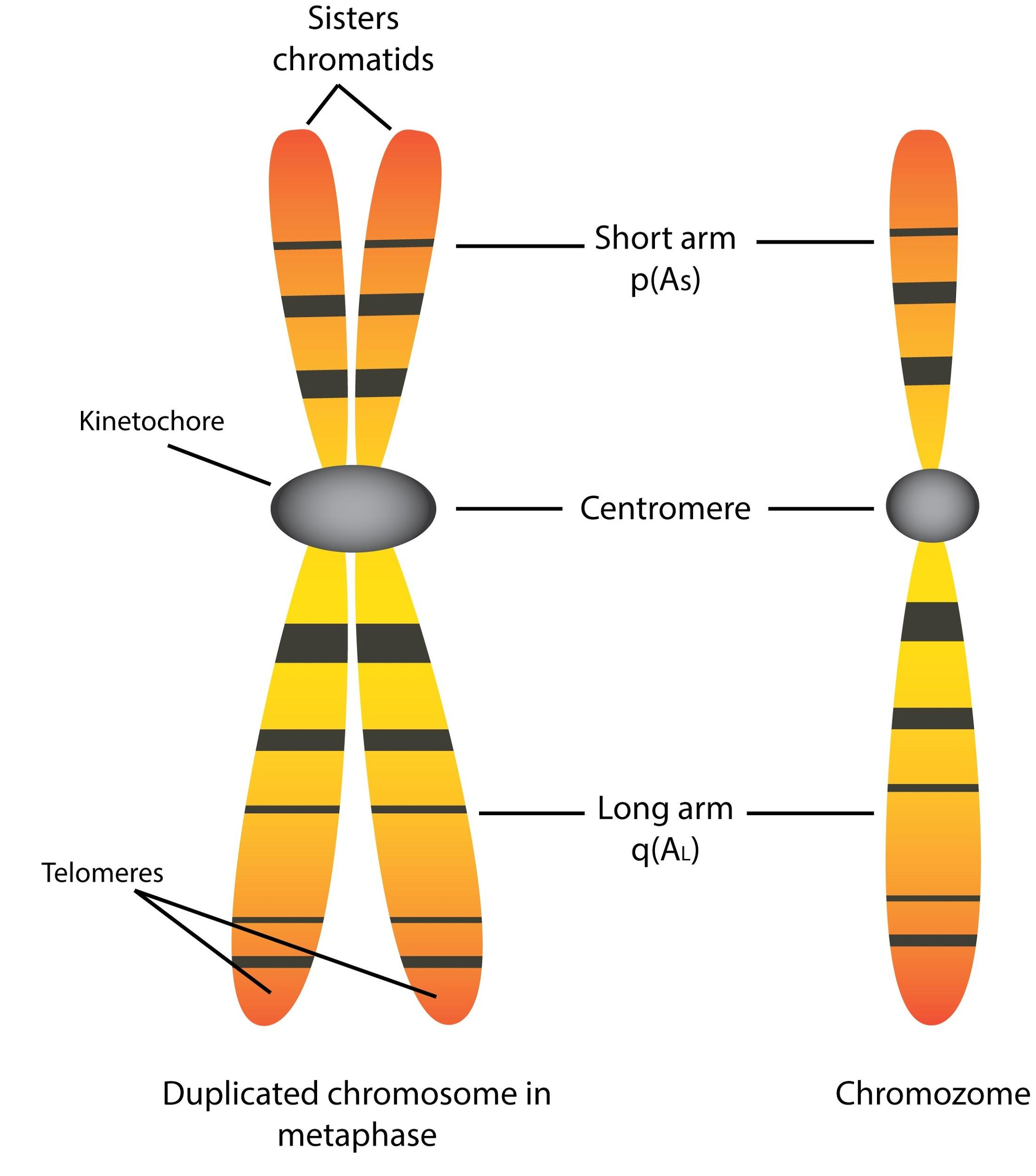
How is DNA packaged into chromosomes and describe the structure of a chromosome? The general structure of somatic chromosomes can be studied best at the metaphase and anaphase of mitosis. Each comprises the following parts: Pellicle and Matrix Chromonemata (Chromatid during Metaphase) Chromomeres Centromere
Learn about types of chromosome, its structure with diagram, its various functions and role associated with the human body and how it differs from gene further in this article. Chromosomes. Chromosome was first discovered by German biologist Walther Flemming. The term 'chromosome' was coined by W. Waldeyer in the year 1888.

Structure chromosome infographics Royalty Free Vector Image
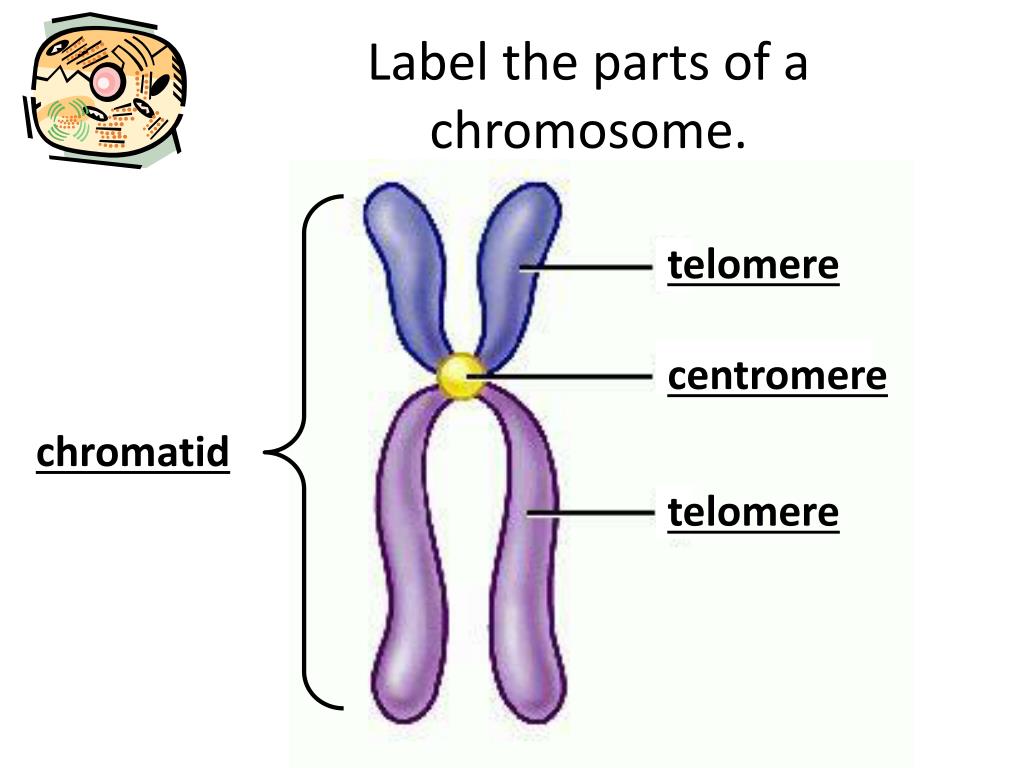
sohaib. 11 years ago. Chromosomes:A threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. Chromatid:Each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division.

Mapping Genomes · Biology
The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events that describes the stages of a cell's life from the division of a single parent cell to the production of two new daughter cells. The mechanisms involved in the cell cycle are highly regulated. Eukaryotic Chromosomal Structure and Compaction

Chromosome Structure Biology for Majors I
In this article we will discuss about the structure of chromosomes with the help of suitable diagram. Chromosome is present as individual bodies in the interphase as well as in the mitosis. The predominant component in the chromosome is DNA molecule. The genes are located in chromosome of the nucleus and can be called as the discrete unit of.
Chromosomes (Location, Structure, Roles in Probability and Application of
A chromosome is a DNA molecule that contains the genetic information for an organism. The chromosomal structure is composed of the organism's DNA and special proteins to form the dense, coiled architecture. The chromosome's tertiary structure is a crucial component in transcription regulation and cellular replication, and division.
DNA Full Form Guide for Beginners to Understand What it Is
Introduction When a cell divides, one of its main jobs is to make sure that each of the two new cells gets a full, perfect copy of genetic material. Mistakes during copying, or unequal division of the genetic material between cells, can lead to cells that are unhealthy or dysfunctional (and may lead to diseases such as cancer).
Chromatid is(a) One half of chromosome(b) Haploid chromosome(c) Complete chromosome(d) Duplicate
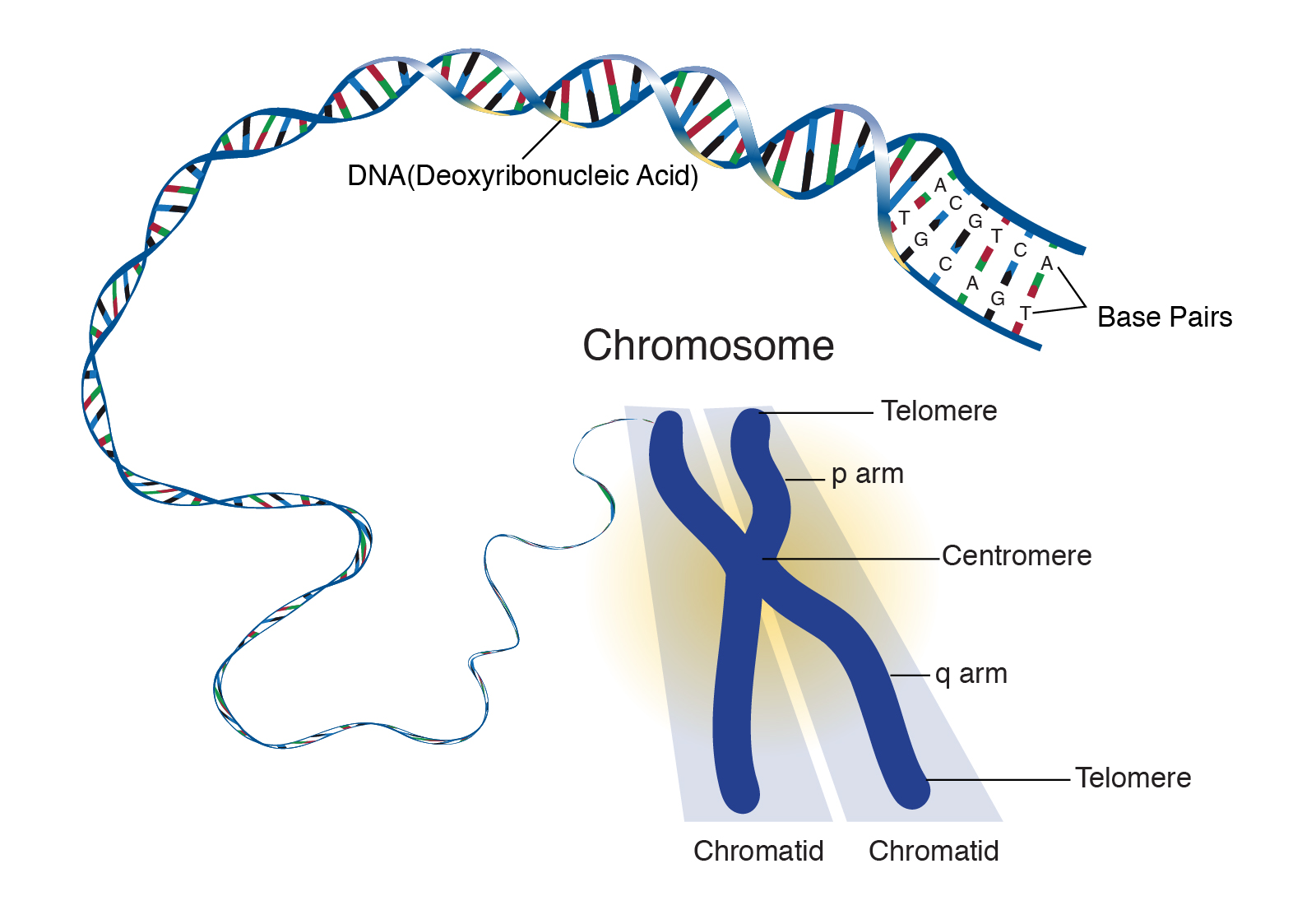
Chromosome structure. Each chromosome is made up of a p and q arm held together by the centromere. The position of the centromere is a distinguishing characteristic and can be classified as metacentric, submetacentric, or acrocentric. The position of the centromere plays a key role in mitotic and meiotic division as chromosomes with skewed.
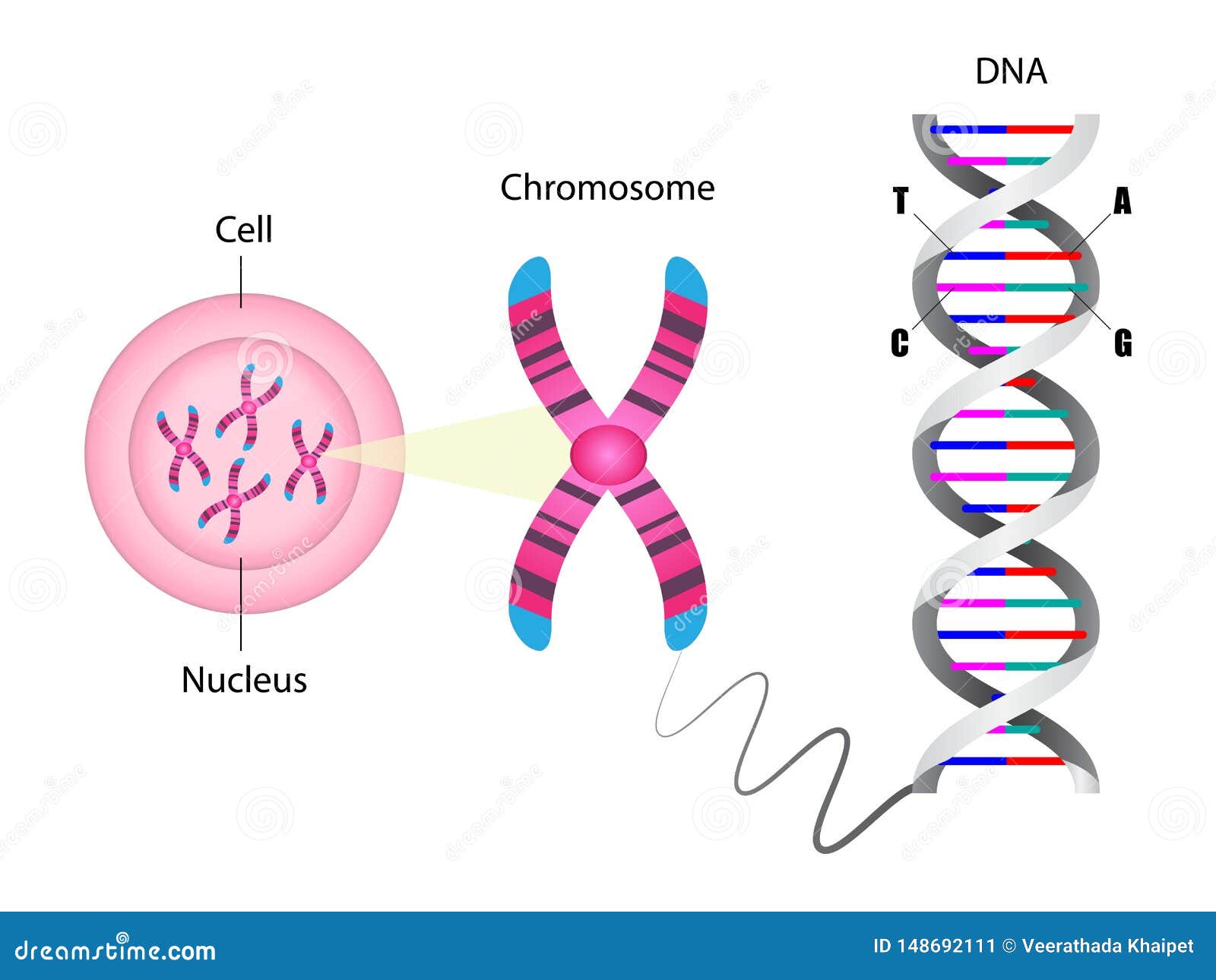
Diagram of Chromosome and DNA Structure Stock Vector Illustration of design, medicine 148692111
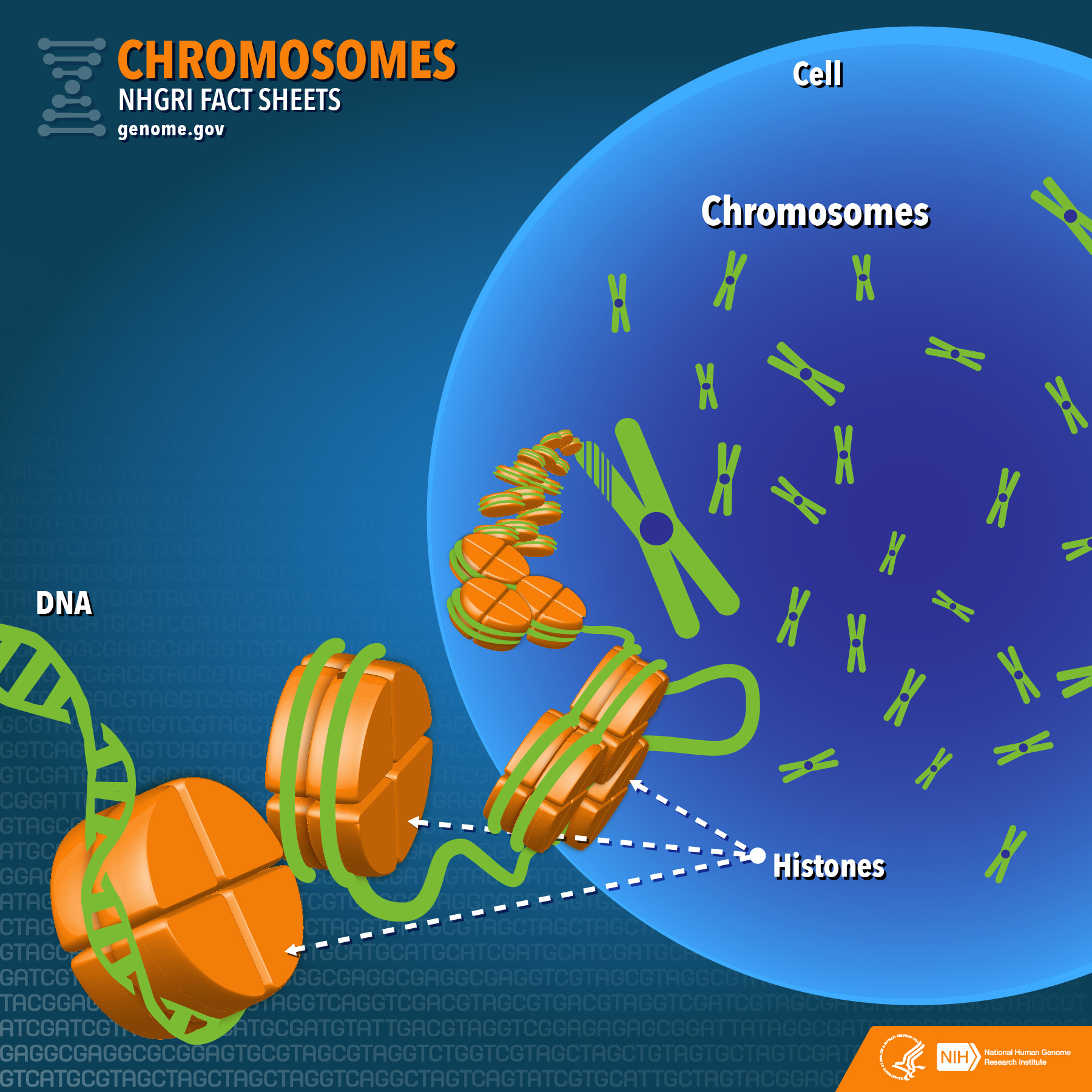
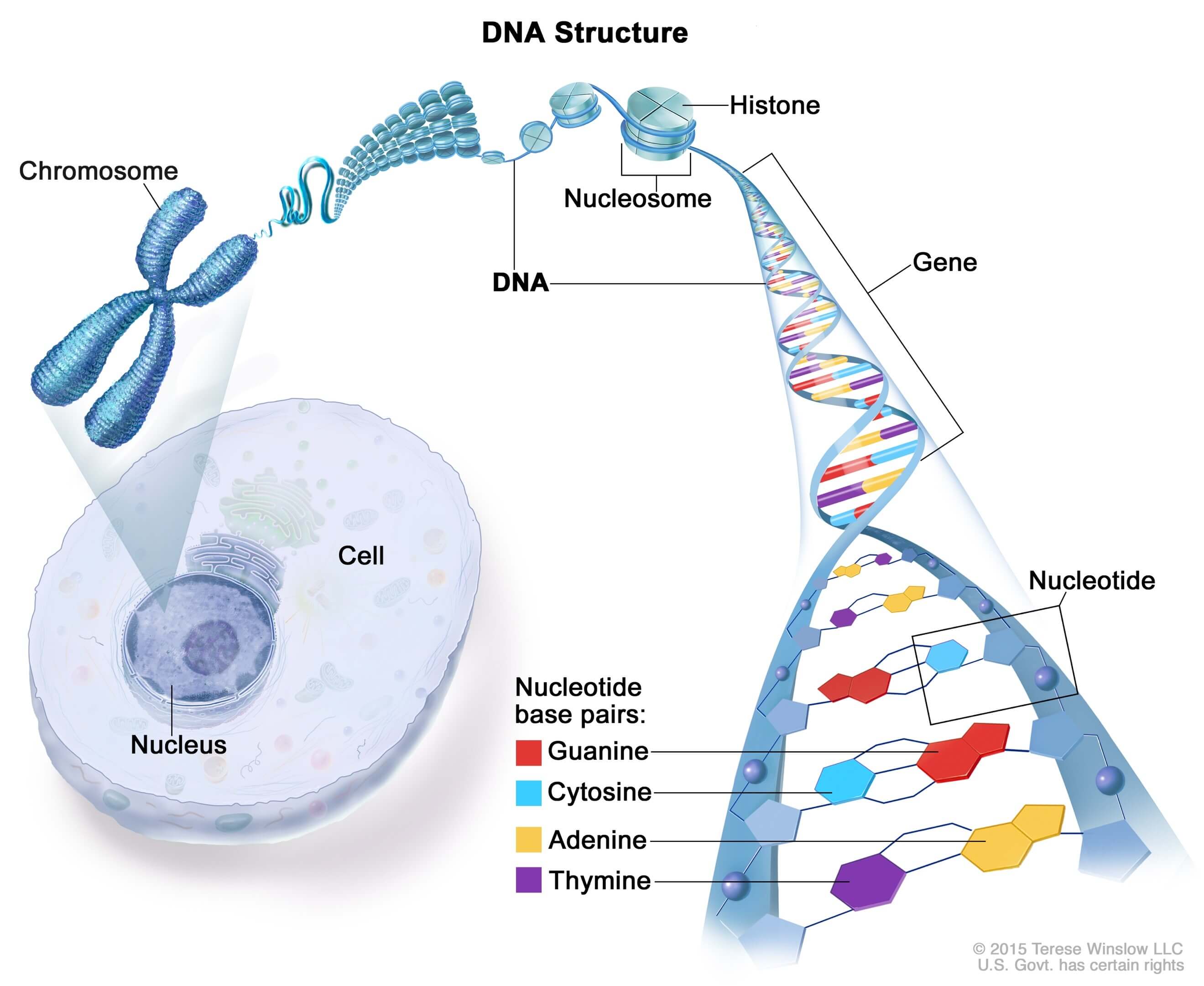
A chromosome is a package of DNA with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA.

Chromosome Structure, Illustration Stock Image C027/6970 Science Photo Library
DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
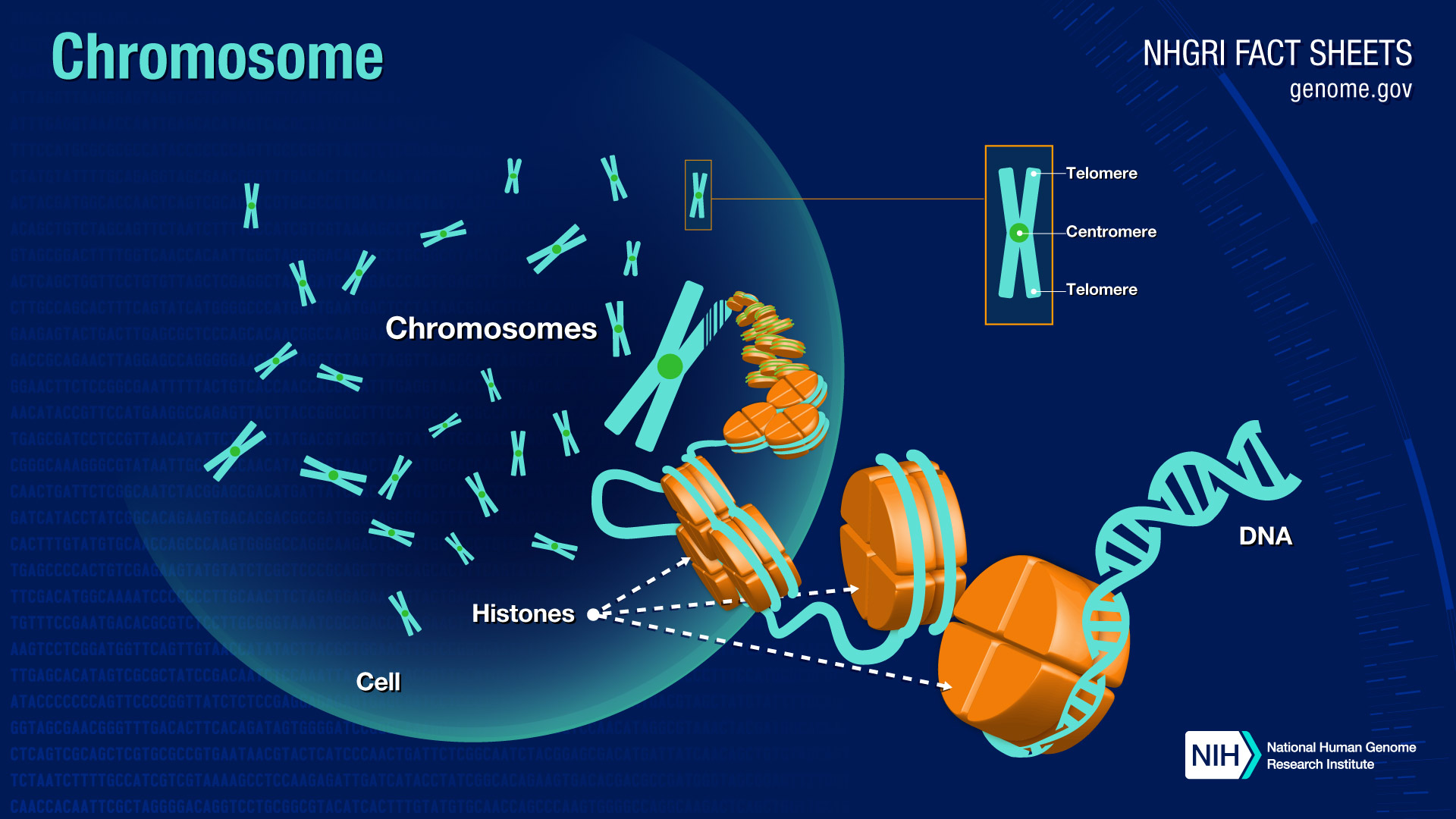
Chromosomes Fact Sheet
Figure 1 shows an idiogram for chromosome 12, a medium-sized chromosome with one long and one short arm. The position of the centromere, which separates the p and q arms, is shown by the hatched area.